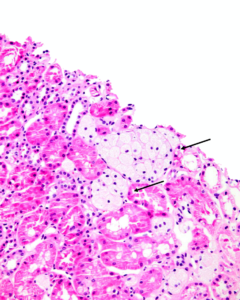
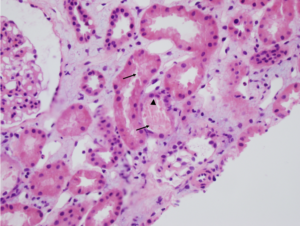
Clusters of interstitial foam cells (arrows) in a kidney biopsy. These are commonly found in biopsy specimens of patients with Alport syndrome, FSGS, IgA nephropathy, and other proteinuric kidney diseases. Image courtesy of Patrick Walker, MD.
Acute interstitial nephritis with associated acute tubular injury. There is interstitial edema and the tubules are not back to back as would be expected, due to the inflammatory and lymphocytic infiltrate in the interstitial compartment. Note the interstitial eosinophils present in the second image (black arrows). Images courtesy of Joseph…
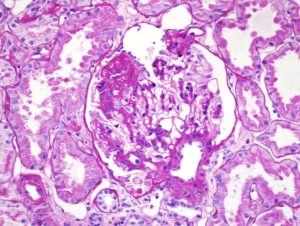
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) in a child presenting with nephrotic syndrome. Image courtesy of Joseph Gaut, MD PhD.
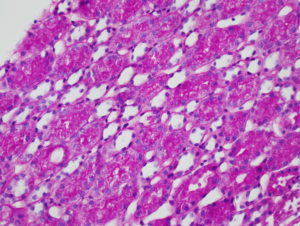
Numerous PAS-positive protein reabsorption droplets in the renal tubules of a child with minimal change disease. Image courtesy of Joseph Gaut, MD PhD.
Acute tubular necrosis (ATN). Note the tubules are not back-to-back due to interstitial edema (Masson trichrome staining, not shown, did not show appreciable fibrosis). There is blebbing and sloughing of tubular epithelial cells (black arrows) with loss of the brush border, as well as flattening of the renal tubular epithelium…
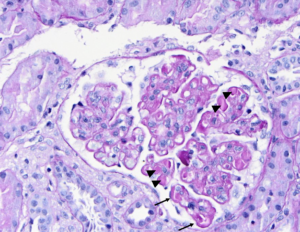
PAS stain of a glomerulus in a patient with SLE nephritis. There is endocapillary and mesangial proliferation, as evidenced by thickened, occlusive capillary loops and increased mesangial cellularity. Note the “wire loop” lesions (arrows) and hyaline thrombi present (arrowheads). Image courtesy of Joseph Gaut, MD, PhD.
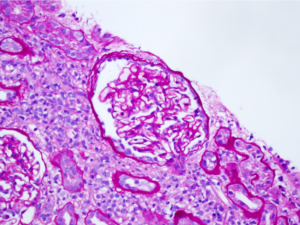
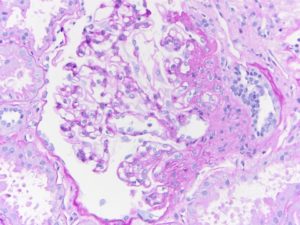
Segmental obliteration of the glomerular capillary lumen in a patient with FSGS. Note the sclerotic portion of the glomerular tuft is adherent to Bowman’s capsule. There is proximal tubular hypertrophy, which can be seen in this condition in response to heavy proteinuria. Image courtesy of Brian Stotter, MD.
- « Previous
- 1
- 2