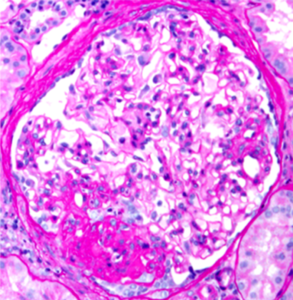
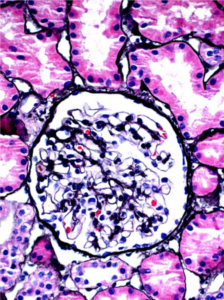
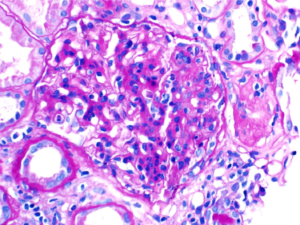
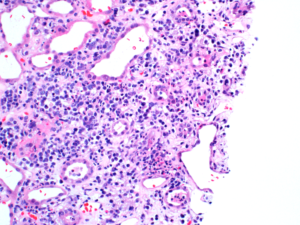
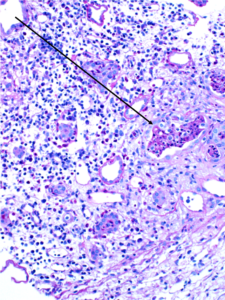
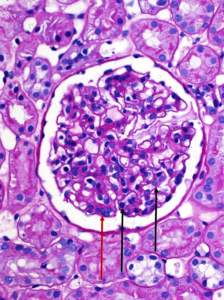
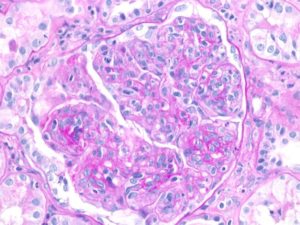
Perihilar variant of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS). Hyaline deposition and sclerosis occur at the vascular pole of the glomerulus. This variant is believed to be a secondary form of FSGS, occurring as an adaptive response to other injuries resulting in loss of functioning nephrons, such as in obesity-related kidney disease.…
Read MoreA normal glomerulus (left) and hypertrophied glomerulus (glomerulomegaly, right). Glomerulomegaly is an adaptive response to decreased nephron number (e.g. prematurity) and/or increased demand (e.g. obesity). Patients with glomerulomegaly may have sub-nephrotic or nephrotic-range proteinuria, but other features of nephrotic syndrome are rare. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, MD.
Read MoreA patient with IgA nephropathy and associated segmental glomerulosclerosis. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, MD.
Read MoreA mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate in a child with acute interstitial nephritis. Image courtesy of Patrick Walker, MD.
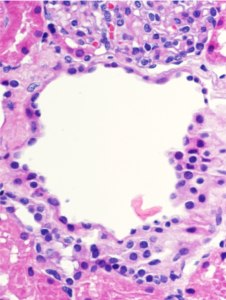
Read MoreWBC casts (black arrows) in a biopsy specimen of a patient with acute interstitial nephritis. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, MD.
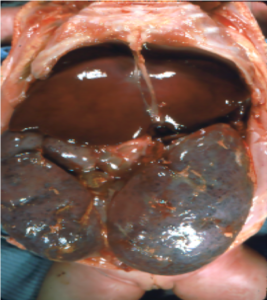
Read MoreGross pathology and low-power light microscopy of kidney tissue in a neonate with ARPKD. The kidneys are enlarged but maintain their reniform shape, and are full of microscopic cysts derived from dilated distal tubules and cortical collecting ducts. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, MD.
Read MoreMicroscopic renal cysts. Note the flattened to cuboidal epithelium lining the cysts. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, MD.
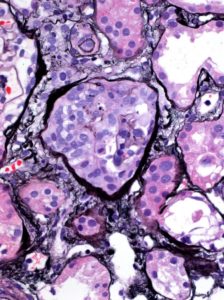
Read MoreA segmental (left, black arrow) and circumferential crescent (right) in a patient with IgA nephropathy. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, MD.
Read MoreA normal appearing glomerulus (left) compared to a glomerulus with endocapillary hypercellularity (right). Note the hypercellular capillary loop (red arrow) compared to the normal capillary lumens (black arrows). This histologic feature can be seen in several glomerular disorders, including IgA nephropathy, post-infectious glomerulonephritis, lupus nephritis, and C3 glomerulopathy. Images courtesy…
Read MoreMembranoproliferative pattern of glomerular injury in a patient with C3 glomerulopathy. This pattern of injury typically has endocapillary proliferation, diffuse capillary wall thickening, increased mesangial matrix, and mesangial proliferation visible on light microscopy, producing a lobular appearance of the glomerular tuft. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, MD.
Read More