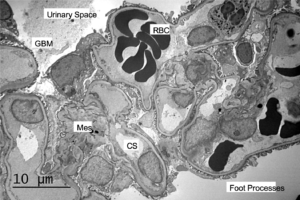
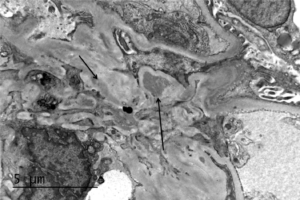
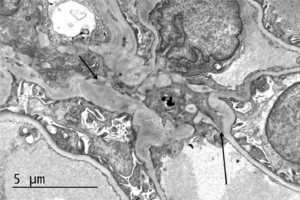
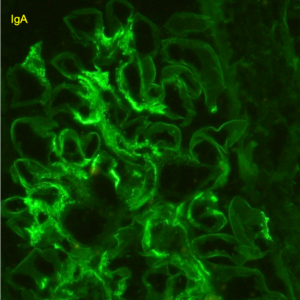
Electron microscopy of a biopsy specimen in a patient with IgA nephropathy. Electron dense deposits can be identified in the mesangium (black arrows), which on immunofluorescence would have predominant or co-dominant IgA staining. Note that although mesangial IgA deposits are classic in IgA nephropathy and IgA vasculitis (former Henoch-Schonlein purpura nephritis), they can be seen in other conditions including infection-associated glomerulonephritis, inflammatory bowel disease, malignancies, sarcoidosis, and certain dermatologic conditions. GBM; glomerular basement membrane. RBC; red blood cells. Mes; mesangium. CS; capillary space. Images courtesy of Patrick Walker, MD.
Posted in General Renal Pathology, Glomerular Diseases